结构化输出
2024 年 12 月 6 日
Ollama 现在支持结构化输出,使得可以将模型的输出约束为由 JSON 模式定义的特定格式。 Ollama 的 Python 和 JavaScript 库已更新以支持结构化输出。
结构化输出的用例包括
- 从文档中解析数据
- 从图像中提取数据
- 结构化所有语言模型响应
- 比 JSON 模式更可靠和一致
开始使用
要将结构化输出传递给模型,可以在 cURL 请求中使用 format 参数,或者在 Python 或 JavaScript 库中使用 format 参数。
cURL
curl -X POST https://127.0.0.1:11434/api/chat -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{
"model": "llama3.1",
"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "Tell me about Canada."}],
"stream": false,
"format": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"name": {
"type": "string"
},
"capital": {
"type": "string"
},
"languages": {
"type": "array",
"items": {
"type": "string"
}
}
},
"required": [
"name",
"capital",
"languages"
]
}
}'
输出
响应以请求中 JSON 模式定义的格式返回。
{
"capital": "Ottawa",
"languages": [
"English",
"French"
],
"name": "Canada"
}
Python
使用 Ollama Python 库,将模式作为 JSON 对象传递给 format 参数,可以是 dict,也可以使用 Pydantic(推荐)通过 model_json_schema() 序列化模式。
from ollama import chat
from pydantic import BaseModel
class Country(BaseModel):
name: str
capital: str
languages: list[str]
response = chat(
messages=[
{
'role': 'user',
'content': 'Tell me about Canada.',
}
],
model='llama3.1',
format=Country.model_json_schema(),
)
country = Country.model_validate_json(response.message.content)
print(country)
输出
name='Canada' capital='Ottawa' languages=['English', 'French']
JavaScript
使用 Ollama JavaScript 库,将模式作为 JSON 对象传递给 format 参数,可以是 object,也可以使用 Zod(推荐)通过 zodToJsonSchema() 序列化模式。
import ollama from 'ollama';
import { z } from 'zod';
import { zodToJsonSchema } from 'zod-to-json-schema';
const Country = z.object({
name: z.string(),
capital: z.string(),
languages: z.array(z.string()),
});
const response = await ollama.chat({
model: 'llama3.1',
messages: [{ role: 'user', content: 'Tell me about Canada.' }],
format: zodToJsonSchema(Country),
});
const country = Country.parse(JSON.parse(response.message.content));
console.log(country);
输出
{
name: "Canada",
capital: "Ottawa",
languages: [ "English", "French" ],
}
示例
数据提取
要从文本中提取结构化数据,请定义一个模式来表示信息。 然后模型提取信息并以定义的 JSON 模式返回数据
from ollama import chat
from pydantic import BaseModel
class Pet(BaseModel):
name: str
animal: str
age: int
color: str | None
favorite_toy: str | None
class PetList(BaseModel):
pets: list[Pet]
response = chat(
messages=[
{
'role': 'user',
'content': '''
I have two pets.
A cat named Luna who is 5 years old and loves playing with yarn. She has grey fur.
I also have a 2 year old black cat named Loki who loves tennis balls.
''',
}
],
model='llama3.1',
format=PetList.model_json_schema(),
)
pets = PetList.model_validate_json(response.message.content)
print(pets)
示例输出
pets=[
Pet(name='Luna', animal='cat', age=5, color='grey', favorite_toy='yarn'),
Pet(name='Loki', animal='cat', age=2, color='black', favorite_toy='tennis balls')
]
图像描述
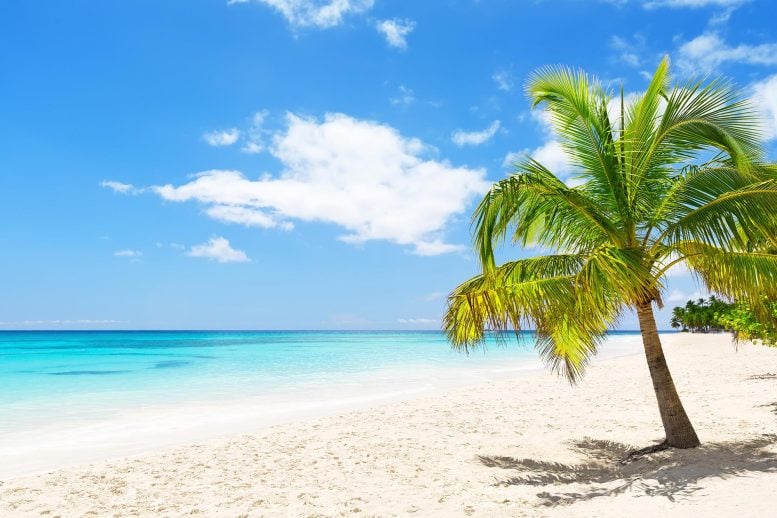
结构化输出也可以与视觉模型一起使用。 例如,以下代码使用 llama3.2-vision 来描述以下图像并返回结构化输出

from ollama import chat
from pydantic import BaseModel
class Object(BaseModel):
name: str
confidence: float
attributes: str
class ImageDescription(BaseModel):
summary: str
objects: List[Object]
scene: str
colors: List[str]
time_of_day: Literal['Morning', 'Afternoon', 'Evening', 'Night']
setting: Literal['Indoor', 'Outdoor', 'Unknown']
text_content: Optional[str] = None
path = 'path/to/image.jpg'
response = chat(
model='llama3.2-vision',
format=ImageDescription.model_json_schema(), # Pass in the schema for the response
messages=[
{
'role': 'user',
'content': 'Analyze this image and describe what you see, including any objects, the scene, colors and any text you can detect.',
'images': [path],
},
],
options={'temperature': 0}, # Set temperature to 0 for more deterministic output
)
image_description = ImageDescription.model_validate_json(response.message.content)
print(image_description)
示例输出
summary='A palm tree on a sandy beach with blue water and sky.'
objects=[
Object(name='tree', confidence=0.9, attributes='palm tree'),
Object(name='beach', confidence=1.0, attributes='sand')
],
scene='beach',
colors=['blue', 'green', 'white'],
time_of_day='Afternoon'
setting='Outdoor'
text_content=None
OpenAI 兼容性
from openai import OpenAI
import openai
from pydantic import BaseModel
client = OpenAI(base_url="https://127.0.0.1:11434/v1", api_key="ollama")
class Pet(BaseModel):
name: str
animal: str
age: int
color: str | None
favorite_toy: str | None
class PetList(BaseModel):
pets: list[Pet]
try:
completion = client.beta.chat.completions.parse(
temperature=0,
model="llama3.1:8b",
messages=[
{"role": "user", "content": '''
I have two pets.
A cat named Luna who is 5 years old and loves playing with yarn. She has grey fur.
I also have a 2 year old black cat named Loki who loves tennis balls.
'''}
],
response_format=PetList,
)
pet_response = completion.choices[0].message
if pet_response.parsed:
print(pet_response.parsed)
elif pet_response.refusal:
print(pet_response.refusal)
except Exception as e:
if type(e) == openai.LengthFinishReasonError:
print("Too many tokens: ", e)
pass
else:
print(e)
pass
提示
为了可靠地使用结构化输出,请考虑: - 使用 Pydantic (Python) 或 Zod (JavaScript) 定义响应的模式 - 在提示中添加“以 JSON 格式返回”以帮助模型理解请求 - 将温度设置为 0 以获得更确定的输出
下一步是什么?
- 公开 logits 以进行受控生成
- 结构化输出的性能和准确性改进
- 采样 GPU 加速
- 除 JSON 模式之外的其他格式支持